Winter Warmth Meets Luxury: Understanding the Key Differences Between Two Popular Fabrics
Both velvet and fleece fabrics offer unique qualities that make them popular choices for different uses. Velvet is a luxurious woven fabric with a dense, soft pile made from silk or synthetic fibres, whilst fleece is a lightweight synthetic material designed for warmth and comfort.
Velvet’s elegant appearance and smooth texture make it a favourite for formal wear and upscale home furnishings. Fleece, with its excellent insulation properties, serves as the go-to choice for casual clothing and outdoor gear.
On This Page
Key Takeaways
- Velvet offers luxury and elegance with its dense pile and smooth texture
- Fleece provides superior warmth and insulation in a lightweight form
- Each fabric requires specific care methods to maintain its unique properties
Comparing Fabrics: Fleece and Velvet
Fleece and velvet represent two distinct textile innovations that transformed the fabric industry. Each offers unique properties in terms of texture, warmth, and appearance.
Historical Background
Velvet fabric emerged as a luxury textile in ancient civilisations, particularly in Eastern cultures. Its production required complex weaving techniques that made it exclusive to nobility and wealthy merchants.
Fleece entered the market in 1979 through Malden Mills (now Polartec) as a synthetic alternative to wool. Engineers designed it specifically to address the limitations of traditional wool garments.
The development of fleece marked a significant shift towards more practical, accessible textiles. Its creation revolutionised outdoor clothing by offering a lightweight, warm alternative to natural fibres.
Fabric Composition and Types
Velvet plush features a longer pile height with a polyester backing, creating its signature soft texture. Traditional velvet can be made from silk, cotton, or synthetic fibres.
Fleece primarily consists of polyester fibres, though some variations include cotton, viscose, or recycled materials. Its knitted construction creates tiny air pockets that trap warmth.
Common velvet types include:
- Crushed velvet
- Stretch velvet
- Silk velvet
- Cotton velvet
Popular fleece varieties include:
- Polar fleece
- Micro fleece
- Double-sided fleece
- Anti-pill fleece
Physical and Aesthetic Characteristics
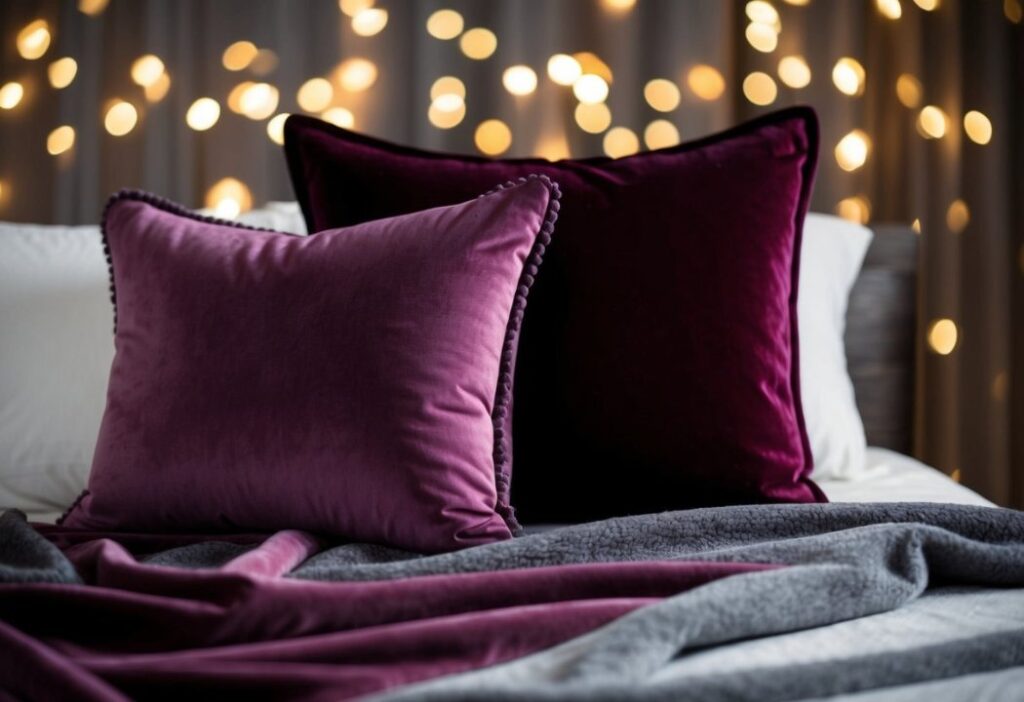

Velvet and fleece showcase distinct textures and visual qualities that make each fabric unique. The two materials differ dramatically in their surface characteristics and how they interact with light.
Texture and Feel
Velvet’s smooth pile creates an exceptionally soft surface that feels luxurious to touch. The short, dense fibres stand upright, creating a plush sensation when running one’s hand across the material.
The fabric requires gentle handling due to its delicate nature. When pressed, the fibres move in a single direction, creating visible marks that can be brushed away.
Fleece offers a different type of softness, with a fuzzy, brushed texture that feels warm and cosy against the skin. Its synthetic fibres create a spongier feel compared to velvet’s sleek surface.
Appearance and Sheen
Velvet’s defining feature is its distinctive shine that changes with movement. Light reflects off the upright fibres, creating a shifting pattern that appears darker or lighter depending on the viewing angle.
Fleece maintains a consistent matte appearance without the dramatic light play of velvet. Its brushed surface scatters light evenly, resulting in a more casual look.
The pile height varies between the fabrics:
- Velvet: 1-2mm short, dense pile
- Fleece: 3-5mm lofted, brushed pile
Production and Manufacturing Processes
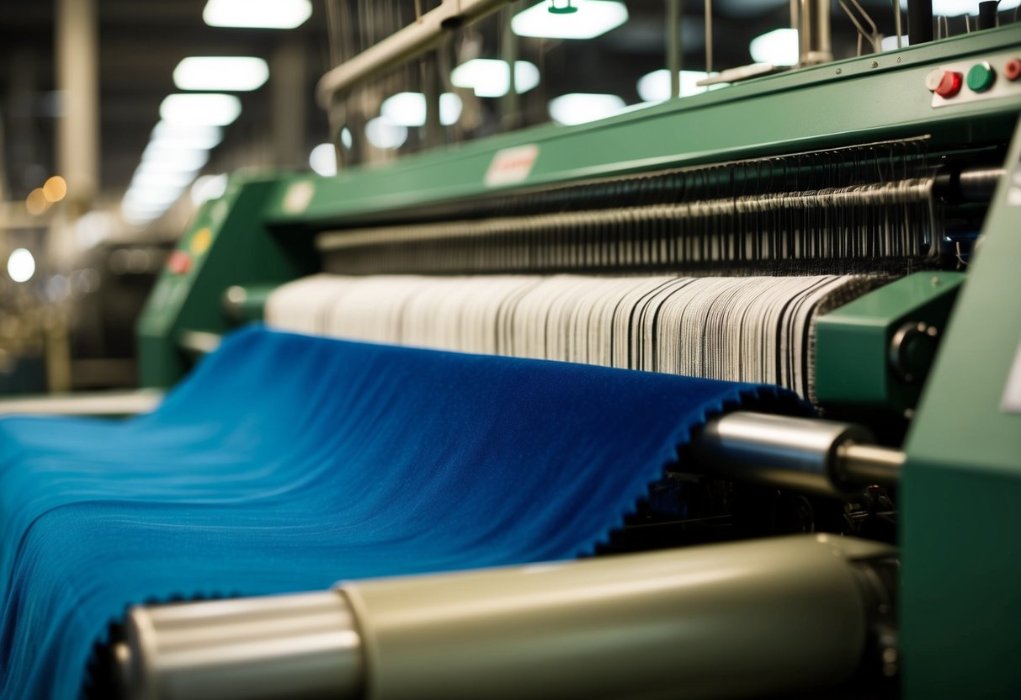

The production of velvet and fleece involves distinct manufacturing techniques using both natural and synthetic materials. Each fabric requires specialised equipment and careful processing to achieve its unique texture and properties.
Textile Production Techniques
Traditional velvet manufacturing relies on a complex weaving process that creates two layers of fabric simultaneously. A specialised loom weaves the fabric with extra yarn that forms the signature pile.
The weaving process involves creating tightly packed rows of yarn that stand upright. These fibres are then cut to create velvet’s distinctive soft surface.
Modern velvet production often combines synthetic fibres with natural materials to create a more durable and cost-effective fabric. The resulting material maintains the classic velvet look whilst being easier to care for.
Synthetic Fabric Manufacturing
Fleece manufacturing begins with petroleum-based materials that are transformed into polyester fibres. These fibres undergo several stages of processing:
- Initial Processing
- Chemical treatment of raw materials
- Formation of synthetic fibres
- Fibre preparation through carding
- Secondary Steps
- Spinning into yarn
- Knitting into base fabric
- Brushing to create soft texture
The final fleece fabric emerges after a careful brushing process that creates its characteristic fuzzy surface. This step is crucial for achieving the warmth and softness fleece is known for.
Functionality and Comfort
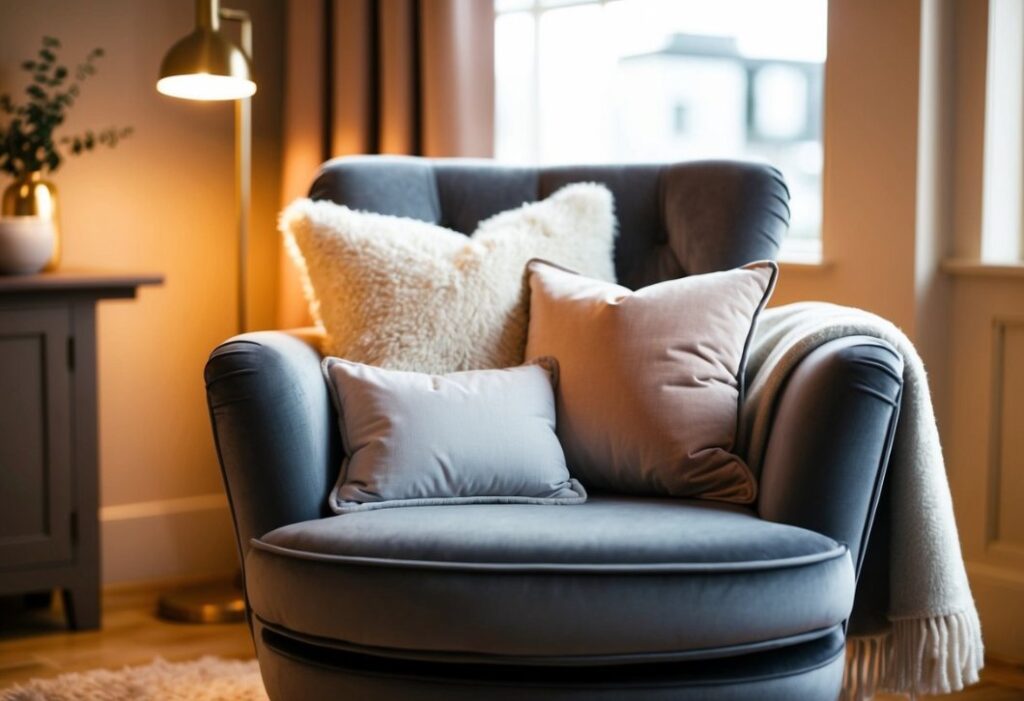

Both velvet and fleece offer distinct advantages in terms of function and comfort, with each fabric excelling in different aspects of wear and use.
Insulation and Warmth
Fleece provides exceptional insulation and traps body heat effectively, making it an excellent choice for cold weather. The synthetic fibres create numerous tiny air pockets that retain warmth.
Velvet offers moderate warmth, though its insulation properties vary based on the fabric composition. Natural silk velvet provides better temperature regulation than synthetic versions.
The pile height affects heat retention in both fabrics. Fleece with a higher pile tends to be warmer, whilst velvet maintains a consistent temperature regardless of pile height.
Breathability and Moisture-Wicking
Modern fleece fabrics excel at moisture management, drawing sweat away from the skin to keep the wearer dry and comfortable. This quality makes fleece particularly suitable for athletic wear and outdoor activities.
Velvet tends to retain moisture more than fleece. Synthetic velvet can feel sticky in warm conditions, whilst natural silk velvet offers better breathability.
The tight weave of velvet can make it less suitable for high-activity situations. In contrast, fleece’s open structure allows air to circulate freely, preventing overheating during physical activity.
Applications and Uses
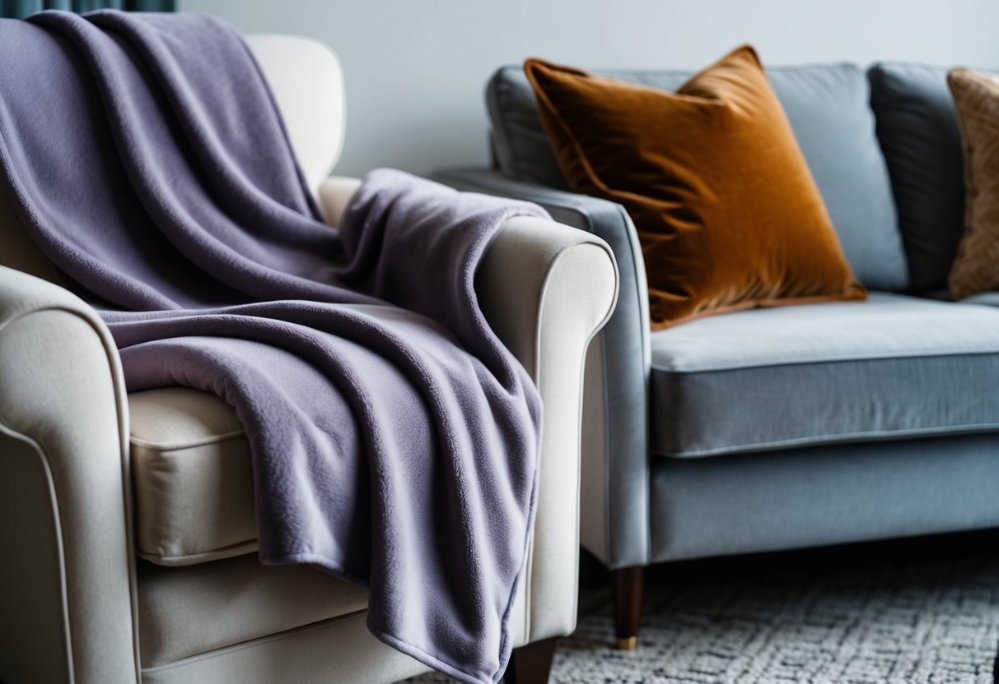

Velvet and fleece serve distinct purposes across fashion and home furnishings. Each fabric’s unique properties make them suited for specific uses in both clothing and decorative applications.
Clothing and Outerwear
Fleece excels in casual wear and sportswear due to its excellent insulation. The fabric’s lightweight nature makes it perfect for winter jackets, jumpers, and outdoor gear.
Fleece maintains warmth even when damp, making it popular for outdoor activities and exercise clothing. Many sports brands use fleece for their cold-weather collections.
Velvet clothing tends towards formal and luxury applications. Evening gowns, formal blazers, and special occasion wear often feature velvet for its elegant appearance.
Home Decor and Upholstery
Cotton velvet works brilliantly for upholstery, adding sophistication to sofas and armchairs. Its durability makes it suitable for high-traffic furniture pieces.
Velvet curtains create a luxurious atmosphere while providing excellent light-blocking properties. The fabric’s natural drape makes it ideal for window treatments.
Fleece blankets offer practical comfort for everyday use. Their affordable price point and easy care make them popular choices for throws and bedding.
Both materials appear in decorative cushions, though velvet tends to feature in formal living spaces while fleece suits casual rooms and dens.
Durability and Maintenance
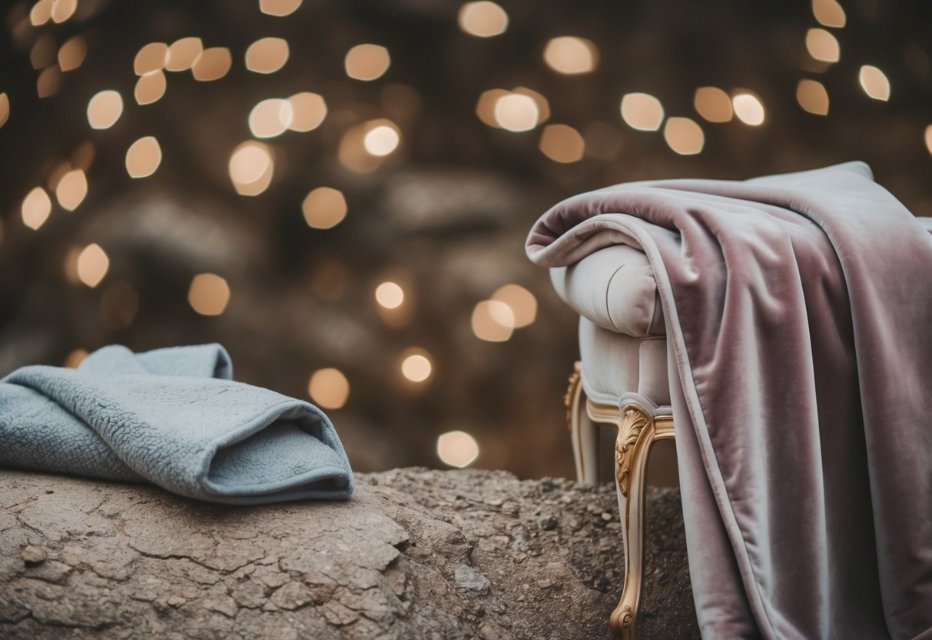

Both velvet and fleece have distinct care requirements that affect their longevity. The right maintenance approach makes a big difference in keeping these fabrics looking their best.
Fabric Longevity
Velvet requires careful handling and can lose its shine with improper care. Traditional silk velvet is quite delicate and prone to crushing or marking.
Synthetic velvet offers better durability whilst maintaining its soft feel. It resists wear and tear more effectively than natural velvet varieties.
Fleece stands up remarkably well to regular use and washing. It rarely shrinks or wrinkles, making it ideal for daily wear.
Care Instructions
Velvet needs gentle washing methods to preserve its pile. Professional dry cleaning is often recommended for natural velvet items.
Synthetic velvet and fleece are machine washable. Use cool water and mild detergent for best results.
Key Care Tips:
- Never iron velvet directly
- Brush velvet pile in one direction after cleaning
- Wash fleece inside out
- Air dry fleece to prevent static build-up
- Store velvet hanging up to avoid crush marks
Environmental Concerns and Sustainability
Both fleece and velvet production methods raise significant environmental questions in modern textile manufacturing. The choice between these fabrics affects resource consumption, pollution levels and waste management.
Impact of Fabric Manufacturing
Traditional velvet made from silk requires intensive farming of silkworms and uses substantial water resources during production. Synthetic velvet creates additional environmental burdens through petrochemical processing.
Fleece fabric typically comes from non-renewable resources like petroleum-based polyester. Its production releases microplastics into waterways during washing cycles.
The manufacturing process for both fabrics requires chemical treatments and dyes. These substances can contaminate local water supplies when not properly managed.
Sustainable Practices in Textile Industry
Several companies now produce fleece from recycled plastic bottles, reducing waste in landfills. This innovative approach helps address plastic pollution while creating functional textiles.
Natural velvet alternatives include organic cotton and bamboo fibres. These materials offer more environmentally responsible options with lower chemical usage.
Emerging Solutions:
- Water recycling systems in manufacturing
- Low-impact dyes and treatments
- Energy-efficient production methods
- Closed-loop manufacturing processes
The textile industry continues to develop new eco-friendly technologies for both fleece and velvet production.
Innovations in Textile Technology
Modern textile manufacturing combines cutting-edge materials with smart technologies to create fabrics that are more functional and sustainable than ever before.
Advanced Textile Materials
New synthetic velvet technologies offer enhanced durability and stain resistance whilst maintaining the luxurious feel of traditional velvet. These fabrics use specially engineered fibres that resist crushing and wear.
Sustainable manufacturing processes now produce materials with minimal waste. 3D-printed textiles create precise patterns and textures, particularly useful in embossed velvet production.
Reversible fleece jackets have evolved through dual-surface technology, which allows different textures and properties on each side. One side might offer wind resistance, whilst the other provides maximum warmth.
Smart Fabric Innovations
Temperature-regulating textiles adapt to body heat and environmental conditions. These materials use phase-change technology to absorb or release heat as needed.
Anti-microbial treatments can now be permanently bonded to fabric fibres. This innovation is particularly valuable in upholstery velvets and performance fleece garments.
Digital sensors woven directly into fabrics monitor:
- Temperature
- Moisture levels
- UV exposure
- Movement patterns
Purchasing and Care Tips
Smart shopping choices and proper maintenance keep both velvet and fleece looking their best for years to come. The right care techniques help preserve texture and appearance.
Selecting Quality Fabrics
Polyester velvet offers excellent durability for everyday use, making it ideal for both formal attire and home furnishings. Look for dense, even pile with no bare patches or irregular patterns.
Cotton velvet provides breathability and natural lustre, perfect for elegant clothing and upholstery. Test fabric quality by running your hand against the pile – it should feel smooth and uniform.
Wool fleece delivers superior warmth and moisture-wicking properties. Quality wool fleece has dense fibres with minimal pilling.
Polyester fleece should have consistent thickness and even colouring. Check for secure stitching and reinforced edges.
Maintaining Fabric Appearance
Velvet requires special care to maintain its luxurious appearance. Use a soft brush to gently remove dust and debris, always brushing in the direction of the pile.
Professional dry cleaning is essential for velvet garments. Store velvet items hanging up to prevent crushing the pile.
Fleece is simpler to maintain, typically allowing machine washing in cold water. Turn fleece garments inside out before washing to prevent pilling.
Avoid using fabric softeners on fleece as they can reduce its moisture-wicking abilities. Air dry fleece items or use low heat settings.
Regular brushing helps maintain the texture of both fabrics. Remove pills from fleece using a fabric shaver.
Frequently Asked Questions
Both fleece and velvet provide unique benefits for different uses in clothing and home furnishings. The right choice depends on factors like warmth needs, cleaning requirements, and intended use.
What are the differences between fleece and velvet fabrics in terms of texture and feel?
Velvet has a luxurious, smooth pile with a sophisticated sheen. Its surface feels dense and elegant to the touch.
Fleece offers a softer, more casual texture with a fuzzy surface. The material feels light and cosy against the skin.
Which material is more suitable for winter apparel, fleece or velvet?
Fleece excels at providing warmth and insulation, making it ideal for winter clothing and sportswear. Its synthetic fibres trap heat effectively.
Velvet, whilst warm, serves better as formal winter wear rather than performance clothing.
What are the primary disadvantages of using fleece fabric?
Fleece can generate static electricity and attract lint or pet hair. The material may pill after repeated washing.
Synthetic fleece requires special care to maintain its insulating properties.
In terms of durability, how do fleece and velvet compare?
Velvet proves more wear-resistant but requires careful maintenance and often needs dry cleaning.
Fleece maintains its properties through regular machine washing but may show wear more quickly with heavy use.
Can fleece or velvet be considered the warmest material for a blanket?
Fleece blankets provide superior warmth due to their excellent insulating properties. The synthetic fibres create air pockets that retain body heat effectively.
Velvet blankets offer moderate warmth but excel more in appearance than thermal properties.
When choosing a sofa covering, what should be considered when comparing fleece and velvet?
Velvet upholstery provides a formal, elegant appearance and resists crushing when properly maintained.
Fleece coverings suit casual spaces but may show wear more quickly and attract dust or pet hair.
Daily cleaning and maintenance prove easier with fleece, whilst velvet requires professional cleaning.
Related Posts: