From Garden to Production: Understanding the Art and Science of Preserving Natural Beauty
Rose petals are the delicate, colourful parts of a rose flower that surround its centre. These soft, fragrant leaves come in various shades, from deep red to pale pink and white. Rose petals are produced naturally as part of the rose plant’s growth cycle, developing as the flower bud opens and blooms.
People have used rose petals for centuries in perfumes, foods, and medicines. Their aromatic qualities make them popular in potpourri and essential oils. In cooking, rose petals add a floral sweetness to dishes and drinks.
Recently, rose petals have found new uses in the textile industry. Rose petal fabric is made from waste rose petals and bushes. This eco-friendly material offers a sustainable option for clothing and accessories.
On This Page
Key Takeaways
- Rose petals are the colourful, fragrant parts of rose flowers used in various products
- These versatile plant parts have applications in perfumery, cuisine, and traditional medicine
- New innovations include rose petal fabrics, offering sustainable alternatives in the textile industry
Botanical Profile of Roses
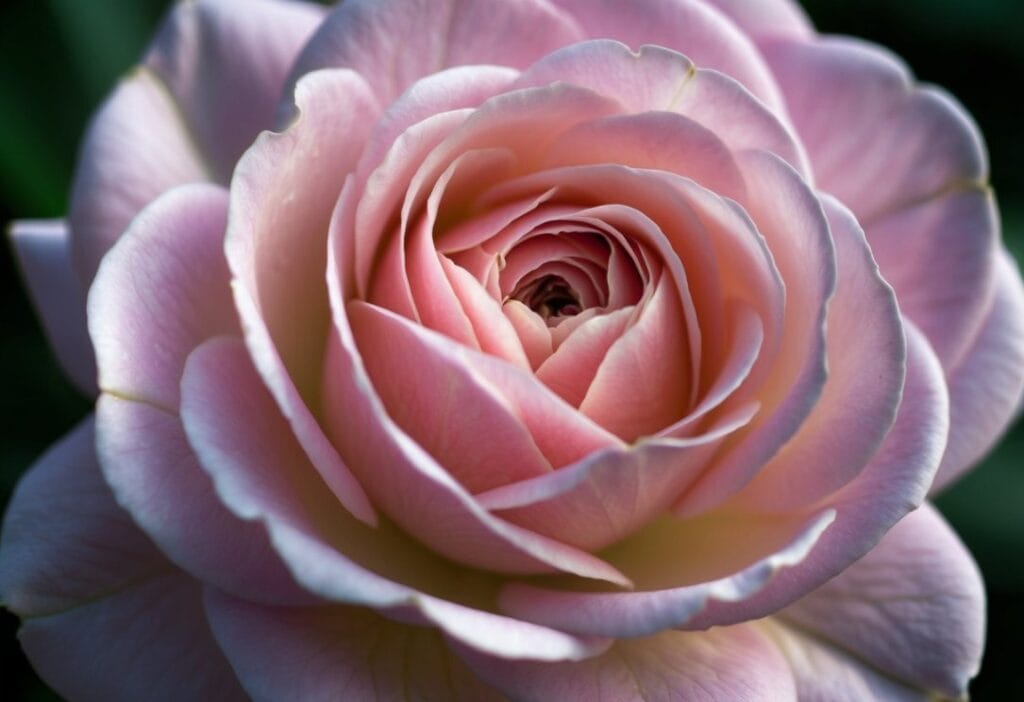

Roses are complex flowers with distinctive petals and diverse varieties. Their structure and characteristics vary widely across different species and cultivars.
Anatomy of the Rose Petal
Rose petals are the colourful, fragrant parts of the flower that attract pollinators. They are modified leaves that form the corolla of the rose. Petals can range from just a few to over 100 in some varieties.
The number and arrangement of petals often determine the rose’s classification. Single roses have 4-8 petals, while double roses may have dozens.
Petals are soft and velvety to the touch. Their shape is typically oval or heart-shaped, with a broader top and narrower base. The edges may be smooth or slightly ruffled.
Rose petals contain pigments that give them their vibrant colours. These can range from pure white to deep red, with various shades of pink, yellow, and orange in between.
Varieties and Characteristics of the Indian Rose Bush
The Indian rose bush, also known as Rosa indica, is a popular ornamental plant. It’s prized for its large, showy flowers and sweet fragrance.
This variety typically produces flowers with 30-40 petals. The blooms are often deep pink or red, though other colours exist.
Indian rose bushes are evergreen in warmer climates. They can grow quite tall, reaching heights of 3-5 metres if left unpruned.
The leaves of the Indian rose bush are dark green and glossy. They’re composed of 5-7 leaflets arranged in an alternate pattern along the stem.
These roses are known for their ability to bloom year-round in suitable climates. They’re often used in gardens, hedges, and for cut flowers.
Cultivation and Harvesting Practices
Rose cultivation involves careful planning and specific techniques. Proper growing conditions and harvesting methods are crucial for producing high-quality rose petals.
Growing Roses in the USA
Rose growing in the USA spans diverse climates. The country’s varied regions offer unique challenges and opportunities for rose gardeners.
In warmer southern states, roses thrive with longer growing seasons. Growers must protect plants from intense heat and pests. Northern states face shorter seasons and cold winters. Gardeners there select hardy varieties and use winter protection methods.
Climate change impacts rose cultivation across the USA. Shifting weather patterns affect bloom times and pest prevalence. Gardeners adapt by choosing resilient varieties and adjusting care routines.
Many American rose farms use sustainable practices. These include water-saving irrigation and organic pest control. Such methods help preserve soil health and reduce environmental impact.
Optimal Conditions and Methods
Roses need specific conditions to produce abundant, healthy petals. Sunlight is crucial, with most varieties requiring 6-8 hours daily.
Well-draining soil rich in organic matter is ideal. A pH between 6.0 and 6.5 supports nutrient uptake. Regular feeding with balanced fertilisers promotes vigorous growth and plentiful blooms.
Proper watering is essential. Roses prefer deep, infrequent watering over frequent light sprinkling. This encourages strong root development.
Pruning plays a vital role in rose cultivation. It shapes plants, removes dead wood, and stimulates new growth. Timing varies by variety, but late winter or early spring is common.
Harvesting techniques depend on the intended use of petals. For fresh petals, pick flowers in the morning when fully open. For dried petals, harvest just before full bloom. Gentle handling preserves petal quality during and after harvest.
Rose Petals in Aromatherapy and Perfumery

Rose petals play a vital role in creating fragrances and promoting well-being. Their sweet scent and therapeutic properties make them a popular choice in both aromatherapy and perfumery.
Extraction of Essential Oils
Rose essential oil is obtained through steam distillation of rose petals. This process yields a light, concentrated oil with a fresh, crisp quality.
Another method is solvent extraction, which produces rose absolute. This form is often considered more luxurious and has a richer scent profile.
The extraction process is labour-intensive. It takes about 4 tonnes of rose petals to produce just 1 kg of rose essence. This explains why rose-based products are often costly.
Different rose varieties yield distinct scents. Damask roses produce a vibrant, slightly spicy aroma, while May roses offer a softer, honeyed fragrance.
Rose Oil and Its Uses
Rose oil is a key ingredient in perfumery, often forming part of the middle or heart notes in a fragrance. Its complex aroma can range from fresh and dewy to deep and velvety.
In aromatherapy, rose oil is prized for its calming and uplifting properties. It’s often used to:
- Reduce stress and anxiety
- Improve mood
- Promote better sleep
Rose oil blends well with other essential oils like lavender, creating balanced and harmonious scents. This versatility makes it a favourite among perfumers and aromatherapists alike.
The oil’s therapeutic benefits extend to skincare. It’s known for its moisturising and anti-ageing properties, making it a popular addition to facial oils and creams.
Rose Petals in Cuisine

Rose petals add a unique flavour and aroma to dishes. They can be used in both sweet and savoury recipes, offering a range of health benefits.
Recipes Incorporating Rose Petals
Rose petals can elevate everyday dishes into something special. They work well in desserts like Turkish delight, where their delicate flavour shines. Chefs also use them in savoury dishes, such as lamb tagines and meat rubs.
Rose petal jam is a popular spread, combining the floral taste with sweetness. For drinks, rose petal tea offers a soothing option. Candied rose petals make lovely cake decorations.
In Middle Eastern cuisine, rose water is a common ingredient. It adds a subtle floral note to rice puddings and baklava.
Health Benefits of Edible Roses
Edible rose petals offer more than just flavour. They contain vitamin C, which supports the immune system. Rose petals also provide minerals that contribute to overall health.
Some studies suggest rose petals may have anti-inflammatory properties. This could help reduce swelling in the body.
Rose petal tea is often used to aid digestion. It may help soothe an upset stomach.
It’s important to use only pesticide-free roses for cooking. Organic roses are the safest choice for edible purposes.
Rose Petals in Traditional Medicine

Rose petals have played a significant role in traditional medicine for centuries. They contain beneficial compounds like antioxidants and vitamin C that support health in various ways.
Usage in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine has long valued rose petals for their healing properties. Practitioners use them to:
- Cleanse and detoxify the body
- Promote blood circulation
- Relieve menstrual discomfort
- Ease digestive issues
Rose petals are often steeped in hot water to make a soothing tea. This drink is thought to calm the mind and reduce stress.
Dried rose petals may also be ground into a fine powder. This powder is added to other herbal remedies or applied topically to treat skin conditions.
Rose Petals for the Immune System
Rose petals can help boost the immune system due to their high vitamin C content. This important nutrient:
- Stimulates the production of white blood cells
- Helps protect cells from damage
- Supports the body’s natural defences
The antioxidants in rose petals also play a crucial role in immune health. They fight harmful free radicals in the body, which can weaken immunity when left unchecked.
To harness these benefits, people often drink rose petal tea or take rose petal supplements. Some herbalists recommend adding rose petals to foods or using rose water as a natural immune booster.
Rose Petal-Based Products and Innovations

Rose petals have inspired various products and innovations. These range from traditional religious items to cutting-edge sustainable textiles.
From Dried Petals to Rosaries
Dried rose petals find use in many products, including rosaries. These prayer beads often incorporate rose petals for their spiritual significance. Craftsmen carefully dry and preserve the petals to maintain their colour and fragrance.
The process of making a rose petal rosary involves several steps:
- Drying the petals
- Grinding them into a fine powder
- Mixing with a binding agent
- Shaping into beads
- Stringing the beads together
Rose petal rosaries are prized for their natural beauty and pleasant scent. They offer a unique alternative to traditional wooden or stone rosaries.
Sustainable Textiles with Rose Petal Fibre
The textile industry has embraced rose petal fibre as an eco-friendly material. This innovative fabric comes from natural waste of rose petals and rose bushes.
Rose petal fibre is a blend of cellulose and rice protein. It’s classified as a bast fibre, collected from the inner bark of plants. This material appeals to environmentally conscious consumers and designers alike.
Advantages of rose petal fibre include:
- Sustainability
- Biodegradability
- Soft texture
- Natural fragrance
Some companies use GOTS certified pigments to dye rose petal fabrics. This ensures the entire production process meets strict environmental and social criteria.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Rose petal fabric offers eco-friendly benefits in textile production. It uses waste materials and requires fewer chemicals than traditional fabrics.
The Role of Plant-Based Fibres
Plant-based fibres like rose petal fibre are gaining popularity in the textile industry. They offer a sustainable alternative to conventional materials.
Rose petal fibre comes from the waste of rose bushes and petals. This reduces landfill waste and gives new life to discarded plant matter.
The production process for rose petal fabric is gentler on the environment. It needs fewer harsh chemicals compared to traditional silk or synthetic fabrics.
Many rose petal fabrics use GOTS certified pigments for dyeing. This ensures the colours meet strict ecological standards.
The Textile Industry and Global Warming
The textile sector contributes significantly to global warming. It produces large amounts of greenhouse gases and uses vast water resources.
Rose petal fabric helps address these issues. It requires less water and energy to produce than many conventional fabrics.
The worsted spinning method often used for rose petal fibre is energy-efficient. This further reduces the carbon footprint of the fabric.
By using natural waste, rose petal fabric promotes a circular economy in the fashion industry. This approach helps minimise environmental impact and resource depletion.
Creation of Rose Water
Rose water is a versatile liquid with a delightful scent. It has many uses in cooking, skincare, and aromatherapy. There are different ways to make rose water at home or commercially.
Traditional Distillation Methods
The oldest way to make rose water is through distillation. This process uses heat to extract the essence from rose petals. You start by placing fresh rose petals in a large pot with distilled water. The mixture is then heated gently.
As the water boils, the steam carries the rose oils upwards. This steam is then cooled and collected. The liquid that results is pure rose water. It’s rich in aromatic compounds and has a strong scent.
At home, you can make a simple version of this. Place a bowl in a pot of rose petals and water. Cover the pot with an upside-down lid filled with ice. As the water boils, the steam hits the cold lid and drips into the bowl.
Modern Techniques and Uses
Today, there are quicker ways to make rose water. One easy method is steeping. This involves soaking rose petals in warm water for several hours. The water absorbs the rose’s scent and properties.
Another method is blending. Fresh or dried rose petals are mixed with distilled water in a blender. The mixture is then strained through cheesecloth.
Commercial production often uses solvent extraction. This method yields a more concentrated product. It’s commonly used in perfumes and high-end skincare items.
Rose water made by these methods keeps its antioxidant properties. It’s used in many products like toners, moisturisers, and food flavourings. Some people also use it as a natural room freshener.
Frequently Asked Questions
Rose petals fascinate many people. They spark curiosity about their origins, uses, and production. Let’s explore some common questions about these delicate floral components.
What constitutes the material of rose petals?
Rose petals are made of plant cells. These cells contain water, pigments, and fragrant oils. The outer layer of cells forms a thin, waxy cuticle that protects the petal.
How is rose petal fabric produced?
Artificial rose petals are often made from fabric. Some use micropeach material for a soft feel. Others use simpler fabrics without the fuzzy texture.
Manufacturers dye the fabric to match real rose colours. They then cut the fabric into petal shapes.
Can you provide traditional recipes that include rose petals?
Rose petal jam is a classic recipe. It combines fresh petals with sugar and lemon juice. Rose water, made by steeping petals in water, flavours many Middle Eastern desserts.
Some cultures add dried rose petals to tea blends. They also sprinkle them on rice dishes for colour and aroma.
What factors contribute to the high cost of rose petals?
Fresh rose petals are delicate and have a short shelf life. This makes them costly to transport and store.
Preserved rose petals can last longer, but the preservation process adds to their cost. The colouring used in preservation can also increase the price.
In which regions do roses originate naturally?
Roses naturally grow in many parts of the Northern Hemisphere. They’re native to Asia, Europe, and North America.
China has a long history of rose cultivation. Many modern rose varieties trace their roots to Chinese species.
What process leads to the formation of petals in flowers?
Petals form during the early stages of flower development. They grow from special cells in the flower bud.
As the bud opens, the petals unfurl. Their shape, size, and colour are determined by the plant’s genes. Environmental factors like light and temperature can also affect petal formation.
Related Post: Facts About Rose Petals in Kids’ Dresses for Wedding Ceremonies: Tradition and Symbolism Explained